
However, Maxwell explained accelerated charged particles release electromagnetic radiation. According to Rutherford’s model, electrons revolve at very high speed around a nucleus of the atom in a fixed orbit. Rutherford’s model does not explain the stability of an atom.One of the limitations of the Rutherford model was also that he did not say anything about the arrangement of electrons in the shell of the atom which made his theory incomplete.Rutherford’s model does not explain the stability of an atom. But we know that atoms do not collapse on their own. This should make the atom very unstable then the atom should collapse. The electrons will be attracted more strongly by the oppositely charged nucleus due to which they will come closer and closer to the nucleus and ultimately the electrons should fall into the nucleus by taking a spiral path. Thus, the energy revolving electrons will decrease gradually and their speed will also go on decreasing. When we apply electromagnetic theory to Rutherford’s atomic model, it will mean that the negatively charged (-ve) particles’ electrons revolving around the nucleus with accelerated motion will lose their energy continuously by radiation.The main limitation of the Rutherford Model of the atom: Limitations of Rutherford Model of the atom The nucleus of the ordinary hydrogen atom does not contain any neutrons. Since the hydrogen atom contains an equal number of protons and electrons, it is electrically neutral. The nucleus is almost at the center of the atom. According to Rutherford’s theory, a hydrogen atom consists of a small nucleus containing one proton and one electron revolving around it.An atom is electrically neutral because the number of protons and electrons in an atom is equal.Electron being negatively charged and nucleus being a densely concentrated mass of positively charged particles are held together by the strong electrostatic force of attraction.The circular paths of electrons are called orbits. The electrons are revolving around the nucleus in circular paths at very high speeds. Rutherford’s model proposed that the negatively charged electrons surround the nucleus of the atom.

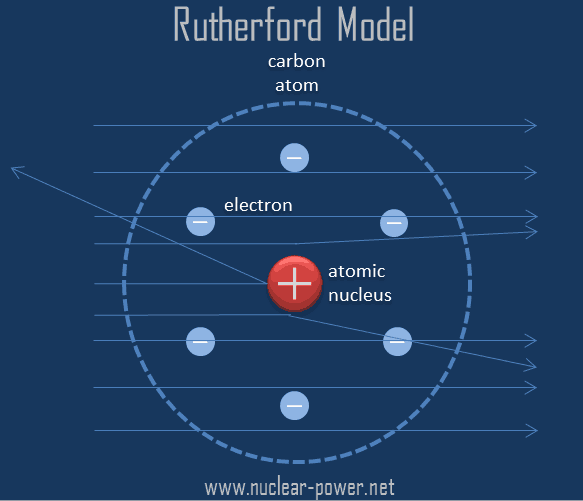
Almost the entire mass of an atom is concentrated in the nucleus. An atom consists of a positively charged, dense, and very small nucleus containing all the protons and neutrons.The Rutherford model of the atom is also called a nuclear atom or planetary model of the atom, a description of the structure of atoms proposed by Ernest Rutherford. 1.2 Rutherford’s Experiment – Discovery of Nucleus.1.1 Limitations of Rutherford Model of the atom.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
